DECOSIS Projector Stand Tripod...
$37.99 (as of July 19, 2024 13:39 GMT +00:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)EJCC 2 Pack Wireless Microphon...
$24.99 (as of July 19, 2024 13:39 GMT +00:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)PQRQP 3 in 1 Wireless Micropho...
$29.99 (as of July 19, 2024 13:39 GMT +00:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Amazon eero mesh WiFi router
$69.99 (as of July 19, 2024 13:39 GMT +00:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Apple 2024 MacBook Air 13-inch Laptop with M3 chip: 13.6-inch Liquid Retina Display, 8GB Unified Memory, 256GB SSD Storage, Backlit Keyboard, 1080p FaceTime HD Camera, Touch ID; Midnight
$863.04 (as of July 19, 2024 13:39 GMT +00:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Amazon Fire Max 11, powerful octa-core tablet with brilliant display, 14-hour battery life, and lightweight durable aluminum design, 128 GB, Gray
$279.99 (as of July 19, 2024 13:39 GMT +00:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)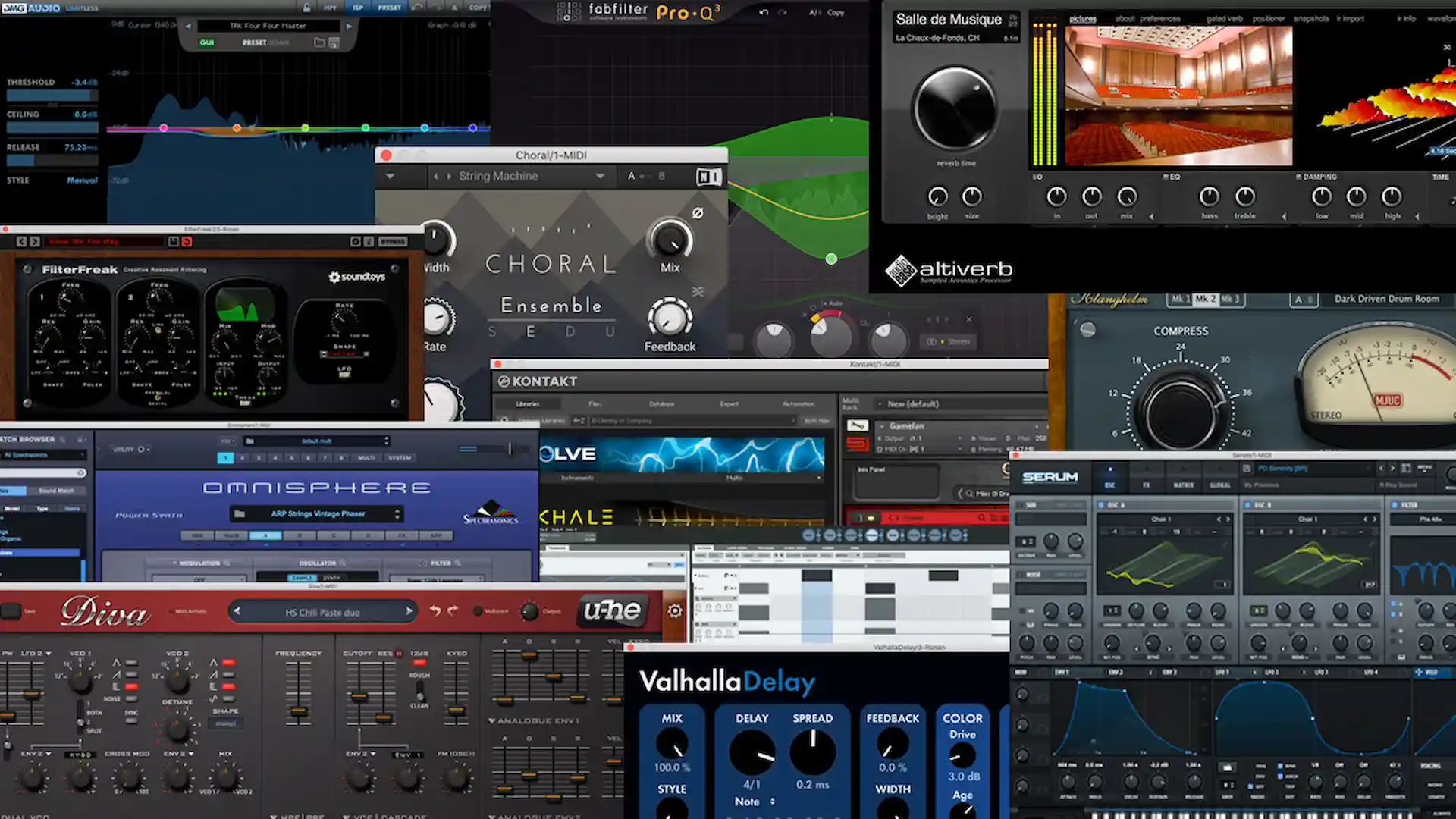
Exploring the World of VST Plugins: Your Gateway to Music Production
What is a VST plugin or Plugin VST
Introduction
What is a VST plugin or Plugin VST Embarking on the journey of music production can be an intimidating experience for beginners. The manuals and tutorials are often filled with intricate terms and cryptic abbreviations. One such term that frequently emerges is VST. If you’ve ever experimented with a DAW like Ableton Live or FL Studio, chances are you’ve dabbled with a VST plugin. However, the true nature of a VST and how to optimize its potential in music creation might still be unclear.
Unveiling the VST Plugin
So, what exactly constitutes a VST in the musical domain? This article aims to unravel the mysteries surrounding this essential production tool. We will elucidate the concept of a VST plugin, explore the advantages of utilizing VST instruments and effects, and guide you through the deployment of VSTs in your own music productions.
Accompany your exploration with Komplete Start, a complimentary package of virtual instruments, tools, and VST plugins designed to ignite your creativity and craft your distinctive sound.
Get Komplete Start Free
Deciphering the VST Plugin
What is a VST?
VST, an acronym for Virtual Studio Technology, acts as a software interface enabling the incorporation of software instruments and effects within a DAW like Ableton Live or FL Studio. Envision your DAW (Digital Audio Workstation) as the central command hub for your productions, while VST plugins serve as valuable supplements offering enhanced functionality for tasks ranging from beat creation to sound design.
Common VST Plugins
Common VST plugins encompass synthesizers, samplers, and audio effects such as reverb and compression. DAWs often come equipped with built-in VSTs, and numerous manufacturers supply VSTs compatible with your chosen DAW.
Revolutionizing Music Production
The advent of VSTs has revolutionized music production. In the pre-’90s era, establishing a music studio posed significant challenges. Each instrument or effect typically manifested as a distinct hardware unit, often expensive, space-consuming, and cumbersome to set up and operate.
The mid-’90s witnessed a paradigm shift as VST technology replicated these hardware units within the software realm. Suddenly, achieving your desired sound became significantly more accessible—simply drag and drop a file into your DAW. This marked the onset of a new era in bedroom production.
Emulation and Innovation
Many widely used VSTs emulate existing hardware units like classic synths and effects. These VSTs typically feature a Graphical User Interface (GUI) allowing manipulation of knobs and sliders, mimicking interaction with the original unit. However, not all VSTs are imitations; contemporary VST plugins often represent imaginative creations absent in the hardware realm.
Distinguishing a Plugin from a VST
While VST is a type of audio plugin, it is not the sole contender in this category. You may encounter AU (Audio Unit) plugins developed by Apple for compatibility with Mac OS systems or Avid’s AAX plugins tailored for Pro Tools.
Many software instruments and effects are available in all three formats (VST, AU, and AAX) with negligible differences in functionality. VST, being the most widely compatible format, reigns as the preferred and extensively utilized option.
Utility of the VST Plugin
VSTs find application across various facets of music production, from synthesizing sounds and triggering samples to processing audio with effects and monitoring using visualizers.
VST plugins facilitate a more rapid, efficient, and cost-effective music-making process than ever before. Software plugins, such as VSTs, typically incur lower costs compared to their hardware counterparts, offer faster operation, and can be conveniently stored on your laptop hard drive, enabling music creation on the go.
Nevertheless, some producers harbor a special affinity for the sound and tactile experience of hardware units, continuing to integrate them alongside VSTs in many modern studios.
A Concise History of VST Technology

Steinberg, the company behind the Cubase DAW, introduced the first VST standard in 1996. Initially, only a few VST effects were available, with the first VST instrument, a polyphonic virtual analog synthesizer named Neon, making its debut in 1999.
Since then, VST technology has evolved progressively, incorporating features like per-note expression and sidechain inputs. The current iteration is VST3, representing the third version of this technology.
Subsequent to VST, other plugin formats emerged, including Apple’s AU in the early 2000s and Avid’s RTAS and AAX. Despite the competition, VST retains its status as the inaugural major audio plugin format and remains the most widely employed.
Functionality of VST Plugins
VSTs are designed for simplicity, boasting swift installation and compatibility with most operating systems and DAWs. However, understanding their workings can enhance your ability to extract optimal performance. Let’s delve into some key aspects.
VST Standard
The versatility of VST plugins stems from their broad compatibility. Numerous audio companies adopt the VST standard for developing plugin instruments and effects. While Steinberg has released several VST standards over the years, the two currently available are VST2 (often referred to as “VST”) and the more sophisticated VST3.
Integration with DAWs
VSTs seamlessly integrate with most major DAWs, such as Ableton Live, Cubase, Logic Pro, and FL Studio. Pro Tools stands as an exception, supporting its proprietary AAX format. However, many VST plugins are available in multiple formats, including AAX, providing flexibility to users. Upon purchasing a plugin, manufacturers typically offer the option to download it in VST, AAX, or AU format.
VST Compatibility
As the most universally compatible audio plugin format, VST operates on both Windows and Mac operating systems, offering a reliable choice for users planning to switch machines. However, as with any software, potential compatibility issues may arise when employing VST plugins. To preempt surprises, it’s advisable to review the developer’s specifications before downloading a plugin.
Varieties of VST Plugins
VST plugins fall into two primary categories, each playing a distinct role in the production process. These categories receive different types of input and often exhibit disparate behavior within your DAW, necessitating an understanding of their differences.
Virtual Instruments
A virtual instrument, or VSTi, serves as a tool for generating sounds, typically receiving MIDI data as input from the piano roll of your DAW or your MIDI keyboard. It outputs audio.
The two main types of virtual instruments are synthesizers, generating audio from scratch based on MIDI input, and sample-based instruments, triggering pre-existing audio segments.
VST synthesizers may emulate classic hardware synths, such as Native Instruments’ FM8, or introduce innovative designs, like Massive X. Sample-based VST instruments, hosted on platforms like Kontakt, excel at emulating real-world instruments and play a central role in modern scoring and composition.
Audio Effects
In contrast to VST instruments, VST effects do not generate audio but instead process and modify incoming audio. They fulfill a role similar to hardware rack FX units, pedals, or effects embedded in mixing consoles.
VST effects cover a spectrum of signal processing tasks, including EQs, compressors, reverbs, delays, and more experimental creations. Similar to virtual instruments, they may emulate beloved hardware or present entirely novel designs.
VST effects receive audio as both input and output. Placing an effect after a VST instrument or another sound source in the signal chain within your DAW allows you to shape the final output.
Utilizing a VST Plugin
Now that you understand what VST plugins are and how they work, let’s look at how to use a VST in your own productions.
- Choose Your VST: There are countless options out there, covering everything from synthesis and sample instruments to various effects. Many cost money, but not all. Komplete Start is a free production suite from Native Instruments featuring 18 instruments and effects alongside over 2,000 studio-quality sounds.
Get Komplete Start Free
- Install Your VST: Most VSTs can be downloaded from the manufacturer’s website or a plugin store such as Plugin Alliance. They come with an installer, meaning they’re quick to get up and running. To make things even easier, Native Instruments VSTs can be downloaded and installed from a single portal, Native Access.
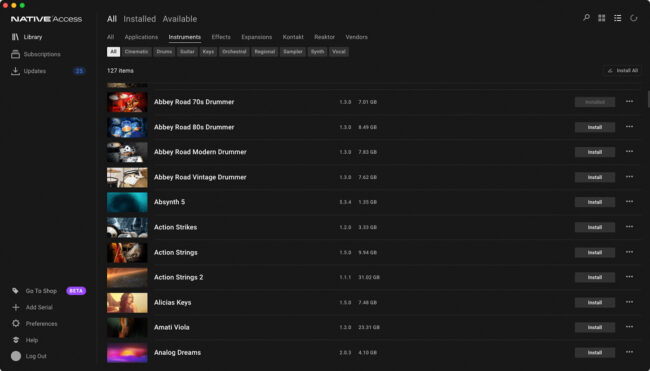
Installing VSTs using Native Access
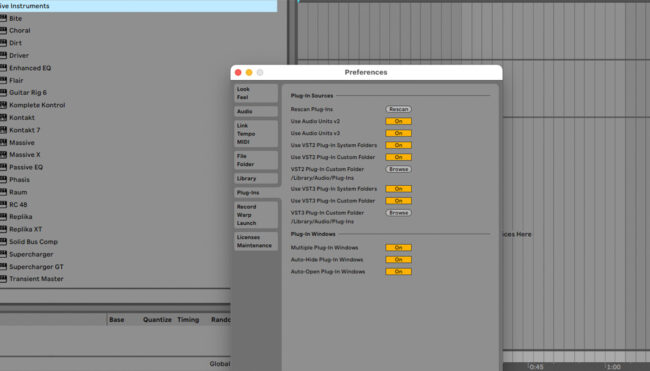
- Locate Your VST in Your DAW: Most DAWs will automatically recognize your newly installed VST. Navigate to the VST folder in the DAW’s browser to locate it. If it’s not there, you can manually scan for new VSTs. In Ableton Live, this is done in the Preferences menu under plugins.
Scanning for VST plugins in Ableton Live
- Use Your VST: Drag it from the browser folder in your DAW onto a channel. If you are adding a VST instrument, it will need to go at the start of the signal chain. If it’s a VST effect, it should come after an instrument or other audio source.
Adding a VST instrument, Native Instruments’ Massive X
- Play and Tweak: Play some chords on your VST instrument. If you have a MIDI controller connected to your DAW, the VST should automatically recognize its input. In Ableton Live, you need to record enable the channel containing the VST. Play a few notes to hear how the VST sounds. If you don’t have a MIDI controller, try adding notes to the piano roll in your DAW.
Tweaking a VST instrument using the GUI
- Customize Your Sound: The starting sound might be basic. Open the VST’s Graphical User Interface (GUI) to tweak its settings. On Ableton Live, this is done by clicking the tool symbol at the top of the VST window. Tweak the dials and sliders on the GUI to get a sound you like. You can also try one of the presets that come with the VST.
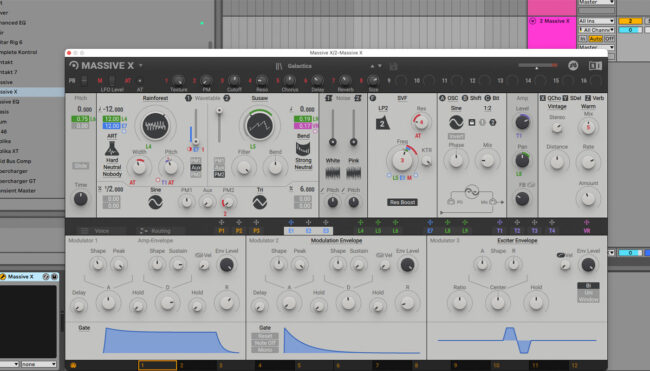
Exploring presets in Massive X
Now that you’ve grasped the essentials of VST plugins and their application, unleash your creativity and delve into the vast world of music production possibilities.
FAQ for VST Plugins
Introduction
Embarking on the journey of music production can be an intimidating experience for beginners. One term that frequently emerges is VST. If you’ve ever experimented with a DAW like Ableton Live or FL Studio, chances are you’ve dabbled with a VST plugin. This FAQ aims to unravel the mysteries surrounding this essential production tool.
What is a VST Plugin?
VST, an acronym for Virtual Studio Technology, is a software interface that allows the incorporation of software instruments and effects within a DAW. VST plugins serve as valuable supplements offering enhanced functionality for tasks ranging from beat creation to sound design.
Common VST Plugins
Common VST plugins include:
- Synthesizers
- Samplers
- Audio Effects (e.g., reverb, compression)
DAWs often come equipped with built-in VSTs, and numerous manufacturers supply VSTs compatible with your chosen DAW.
How Have VSTs Revolutionized Music Production?
Before the ’90s, music studios required distinct hardware units for each instrument or effect. VST technology replicated these hardware units within software, making music production more accessible and efficient. This marked the onset of a new era in bedroom production.
Types of VST Plugins
- Virtual Instruments (VSTi)
- Generate sounds, typically receiving MIDI data.
- Examples: Synthesizers, Sample-based instruments.
- Audio Effects
- Process and modify incoming audio.
- Examples: EQs, compressors, reverbs, delays.
How to Use a VST Plugin
- Choose Your VST: Options range from synthesis and sample instruments to various effects. Many are free, like Komplete Start from Native Instruments.
- Install Your VST: Download from the manufacturer’s website or a plugin store. Use an installer for quick setup.
- Locate Your VST in Your DAW: Most DAWs will automatically recognize your newly installed VST. If not, manually scan for new VSTs in the DAW’s preferences.
- Use Your VST: Drag it from the browser folder in your DAW onto a channel.
- Play and Tweak: Play some chords or notes, then use the VST’s GUI to tweak its settings or try presets.
Advantages of Using VST Plugins
- Flexibility: Allows professionals to refine the presence of vocals, balance individual instruments, and address issues without affecting the entire mix.
- Detailed Control: Enables precise adjustments, resulting in refined and personalized productions.
- Cost-Effective: Software plugins typically incur lower costs compared to hardware counterparts and offer faster operation.
VST Compatibility
VST is the most universally compatible audio plugin format, operating on both Windows and Mac systems. Always review the developer’s specifications to ensure compatibility with your DAW and system.
A Concise History of VST Technology
Steinberg introduced the first VST standard in 1996. The current iteration is VST3, which represents the third version of this technology. VST retains its status as the most widely employed audio plugin format.
Conclusion
VST plugins facilitate a more rapid, efficient, and cost-effective music-making process. By understanding and utilizing VSTs, you can significantly enhance your music production capabilities. Get started with Komplete Start, a free production suite from Native Instruments, and explore the potential of VST plugins in your own productions.
- DAVID GUETTA AND ARMIN VAN BUUREN
- Anyma to Make History in Las Vegas
- Waves V15 with StudioVerse
- Moog Spectravox Moog Semi-Modular Line
- The AI Revolution in Music: From Creation to Distribution











